+86-13777012108
(WhatsApp/WeChat)
1. Basic lighting
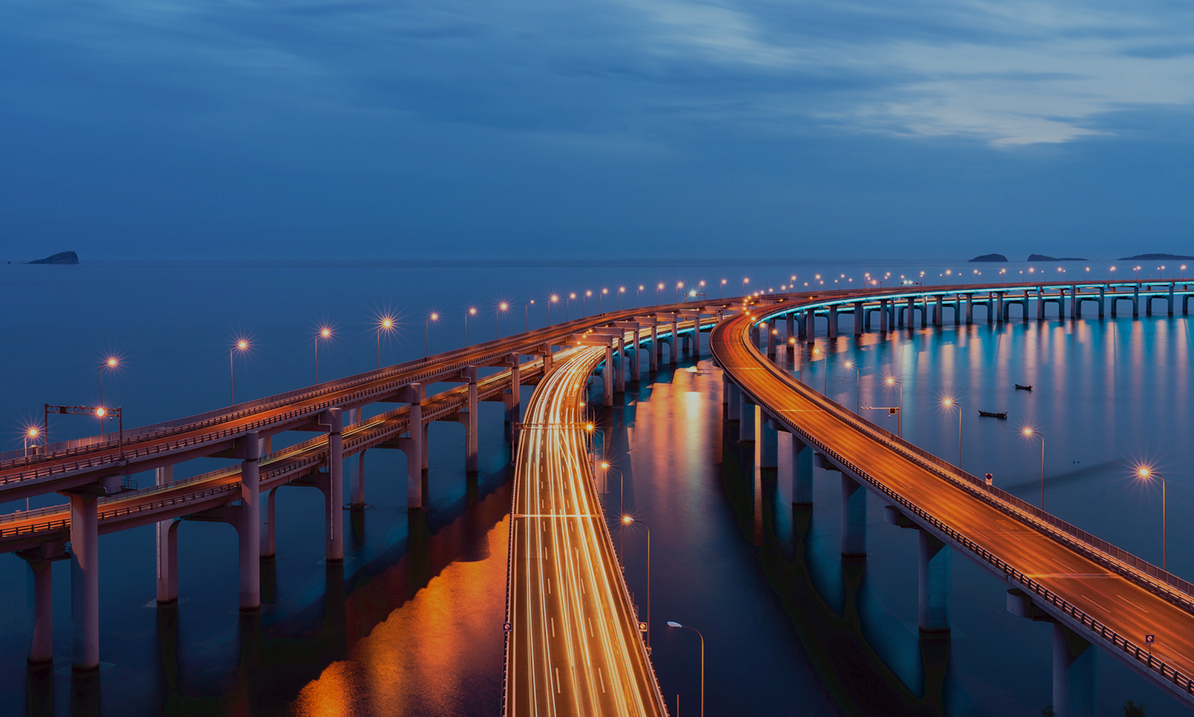
Road lighting: Install street lights on both sides or in the middle of the street to provide sufficient lighting for pedestrians and vehicles to ensure safe passage at night.
Sidewalk lighting: Install low column lights or wall lights on the sidewalk or pedestrian street to facilitate pedestrians to walk at night.
Intersection lighting: Strengthen lighting at intersections or busy traffic areas to improve visibility and reduce traffic accidents.
2. Safety lighting
High-brightness lighting: Install high-brightness lamps in accident-prone areas (such as curves, tunnel entrances, and bridges) to remind drivers to pay attention to safety.
Emergency lighting: In the event of power outages or emergencies, lighting is provided through backup power or solar lights to ensure street safety.
Monitoring auxiliary lighting: Provide sufficient light for surveillance cameras on the street, improve nighttime monitoring effects, and enhance public security management.
3. Energy saving and environmental protection
LED lamps: LED street lights are widely used because they are energy-saving, long-life, and high-brightness, which are suitable for long-term street lighting needs.
Solar street lights: Install solar street lights in sunny areas, charge during the day, and illuminate at night to reduce energy consumption.
Intelligent dimming system: Automatically adjust the brightness of street lights according to traffic flow and natural light intensity to avoid energy waste.
4. Beautification and decoration
Landscape lighting: Install decorative lights in green belts, parks, or squares on both sides of the street to highlight the landscape features and enhance the city's image.
Festival lighting: Use colored lights, light strips,s or projection lights during festivals or celebrations to create a festive atmosphere.
Landmark lighting: Design characteristic lighting for urban landmark buildings or sculptures to enhance nighttime visual effects.
5. Intelligent lighting system
Remote control: Real-time monitoring of street light status through intelligent systems, remote adjustment of brightness and switches, and improved management efficiency.
Fault detection: The intelligent system can automatically detect street light faults, promptly notify maintenance personnel to repair them, and reduce safety hazards.
Traffic flow sensing: Dynamically adjust the brightness of street lights according to traffic flow and reduce the brightness during low traffic hours to save energy.
6. Traffic guidance
Signal light linkage: Street lights are linked with traffic signal light systems to ensure smooth and safe traffic at night.
Lane indicator lighting: Use ground or wall lights to indicate the direction of the lane, helping drivermaintainin the correct driving route on complex roads.
Pedestrian crossing lighting: Set up special lighting at zebra crossings or crosswalks to remind vehicles to pay attention to pedestrians.
7. Maintenance and management
Regular maintenance: Regularly check lamps and circuits to ensure the normal operation of street lights and avoid safety hazards caused by failures.
Waterproof and dustproof design: Choose waterproof and dustproof lamps suitable for outdoor use to extend their service life.
Energy-saving transformation: Gradually replace traditional high-pressure sodium lamps with LED lamps to reduce energy consumption and maintenance costs.
Summary
The application of lamps in streets not only provides basic lighting but also involves safety, energy saving, intelligent management, and beautification. It is an important facility to ensure nighttime traffic safety and enhance the image of the city. Through reasonable design and advanced technology, street lighting systems can effectively improve energy efficiency and enhance citizens' nighttime travel experience.

 English
English Español
Español